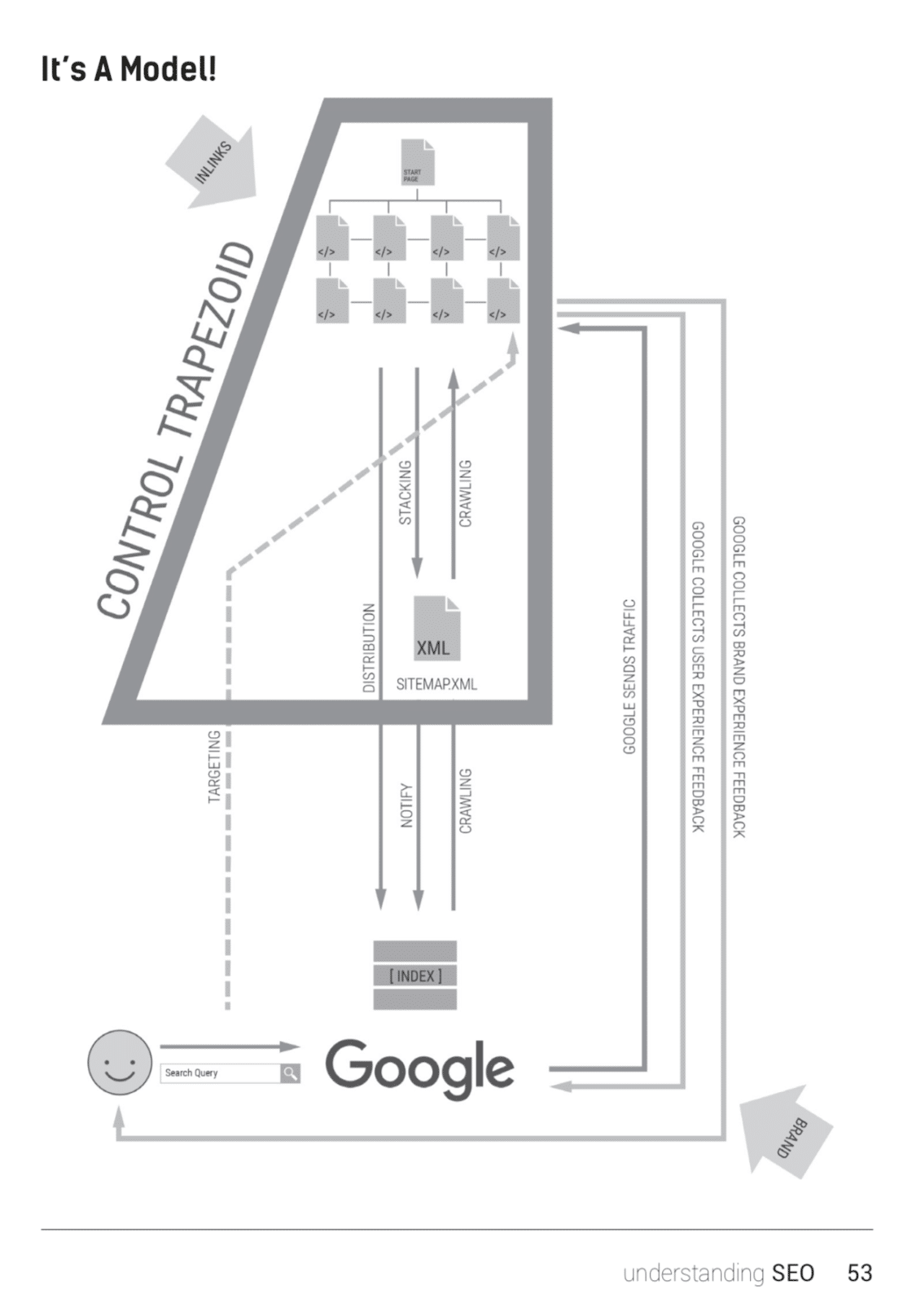
This list covers the basic concepts of the systematic SEO approach. Some concepts (i.e.: search intent, targeted pages, main content, QC) will need deeper understanding of the topic, so I really recommend my book aptly named “Understanding SEO” if you want to get the full picture. It’s as short as possible, I tried to skip all parts that people do not read. Check it out on Amazon (DE / US / UK) or as PDF & epub on Gumroad.
Even without this context I hope you can extract lots of value out of the following (check)list.
SEO
- SEO – Search Engine Optimisation – is the business of getting found.
- SEO is the business of getting found online.
- SEO is all business activities with the goal of getting found online.
Getting found online means in on all western online markets, Google.
SEO is a business activity like many others. SEO is a choice. Nobody is forcing you to do SEO, but if you want your business, your value proposition to get found online and do not want to depend on chance, SEO is the way to go.
SEO works in these parts of an organization
- Development
- Content
- Marketing
- Data
Non of these parts is optional. I.e.: if the website is technical not optimized or search engine friendly (i.e. Google can not render the website) then whatever you do on the content side does not or hardly matter. If your website is technical optimized but your content does not fulfill the search intend of the user you will never perform long term. If your users hate you and do not click you when they see you in the search results, you will always underperform (and you need to work on your positioning and marketing).
Content might be part of the product of the business (i.e. a newspaper, a real estate listing website, …) or it might be part of the marketing activities of the business (i.e. company blog, landingapges).
Systematic SEO is system and data driven. You need to know what happens, so you always will need data.
The SEO Platform
A SEO platform, the so called websites, must consist out of these parts.
- Targeted Pages (Pages that you want to get found for something specific).
- Targeted Detail Pages (show one thinkg i.e. one article, one job listing, ..)
- Targeted List Pages (shows a list of things i.e. list of article, list of job listing, …)
- Distribution (Sitemap.xml)
- Startpage
- Everything else is Ballast / dead weight.
If the SEO Platform is optimized, these SEO Business Cases are possible.
SEO Business Cases
- If we add x% more targeted-pages to our site, we gain y% more traffic.
- If we update x% of our pages, we gain z% more traffic.
- If we make the user experience of our site better, our traffic gets more sustainable.
- If we gain more brand recognition, our traffic gets more sustainable.
These leads to these SEO Processes.
SEO Processes
- How do we create x% more targeted-pages with valuable, unique content? (detail pages and list pages)
- How do we add content/update x% of our targeted-pages?
- How do we assure that our site gets better usage values?
- How do we assure that our site gets more brand recognition?
Processes are formulated as questions as the answers to these questions always differ per company / organisation.
Targeted Pages
Optimized targeted pages must fuflill these requirements.
Onpage
- an HTML page
- targeted at one site wide unique dominant phrase
- fulfills the “job to be done” search intent of the person who searches for that phrase
- fulfills a business utility
- reachable via exactly one URL (see URL-rules)
- hosts unique content or a unique collection of content
- content that has to fulfill a pre-defined quality criteria (the QC)
- uses exactly one language
- links to other targeted pages
- gets linked from at least 1 other targeted page
- all rendering necessary resources (js, css, images) are accessible
- everything visible above fold and the main content is HTML delivered by the server displays the content and links visible without user interaction
- is listed in the sitemap.xml
The QC, the quality criteria, is an internal metric how you determine a good page. The QC should be defined per page type. Do not create pages that do not fulfill your internal QC (a.k.a. do not create pages that you think are bad).
URL-rules
- URL-Rule 1: unique (1 URL == 1 resource, 1 resource == 1 URL)
- URL-Rule 2: permanent (they do not change, no dependencies to anything)
- URL-Rule 3: manageable (equals measurable, 1 logic per site section, no complicated exceptions,
- no exceptions)
- URL-Rule 4: easily scalable logic
- URL-Rule 5: short
- URL-Rule 6: with a variation (partial) of the targeted phrase
URL-Rule 1 is more important than 1 to 6 combined, URL-Rule 2 is more important than 2 to 6 combines, … URL-Rule 5 and 6 are a trade-of. 6 is the least important. A truly search optimized URL must fulfill all URL-Rules.
My preferred URL structure is:
- https://www.example.com/%short-namespace%/%unique-slug%
- https:// – protocol
- www – subdomain
- example – brand
- .com – general TLD or country TLD
- %short-namespace% – one or two letter that identify the pagetype, no dependency to any site hierachy
- %unique-slug% – only use a-z, 0-9, and – in the slug, no double — and no – or – at the end. Only use “speaking slugs” if you have them under your total editorial control.
i.e.: https://www.example.com/a/artikel-name, https://www.example.com/c/cool-list, https://www.example.com/p/12345 (does not fulfill the least important URL-Rule 6), https://www.example.com/p/12345-prouct-name
Onsite Internal interlinking
- Every targeted page has at least one link from another targeted page.
- Every targeted page must be reachable through a click-path starting from the start page.
- More important targeted pages have more links than less important targeted pages.
- Most important targeted pages have a static link from the startpage.
- Ever targeted page must have the chance to get at least once a link from the startpage.
- We only link systematically to the canonical URL.
- We do not link systematically to dead weight.
- Hidden (i.e.: after user interaction, drop-downs) links do not count as votes.
Speed
- Targeted pages should reach green, but at least 80 points plus, on Page Speed Insights.
- In Google Search Console crawling report the average response time for Googlebot Smartphone should be between 200ms to max 400ms.
3 SEO Tests
To guarantee that Google can crawl and render your pages, the targeted pages muss pass these 3 tests. If your pages pass these 3 tests you are doing 80% of technical SEO right.
- Page Speed Insights: minimum score of 80 (still orange) / preferrably 90 (green) for mobile + sensemaking screenshots for mobile + desktop!
- “JS turned off” Test:
- Above fold and main content must be visible on the site with JS turned off!
- Whole site must be navigate-able with JS turned off! (Visible links must be real links).
- Google Search Console -> Inspect URL -> Test Live URL -> View Tested Page -> Screenshot must show correctly rendered mobile page with the content visible!
- No overlays of any kind i.e. privacy / cookie-overlay!
- Images below fold (non-visible) might get lazy loaded)
Targeting
- every page needs a targeted phrase, “something” we want the page to get found for.
- one page, one unique (per site) dominant targeted phrase
Targeting Elements
- URL: should include a short variation (partial) of the targeted phrase, see URL-Rules
- Meta-<title>: ~80 characters + brand, must include the targeted phrase, should encourage click-through.
- Meta description: ~160 characters or more, must be unique per page, should include a number. The meta-description is pure marketing and is not seen as content by the search engine.
- Headline 1: main headline of a page visible above fold, best one per page, should include a variation of the targeted phrase
- Above fold main content images:
- Filenames: should include a short variation of the targeted phrase
- Alt text: descriptive, about 5 words, should include a descriptive variation of the targeted phrase
- Anchor text: links to this targeted page should include a sense-making short variation of the targeted phrase (Not: “click here”, “read more”)
Content
Onpage content must be unique (internally and externally) or at least a unique combination of content (seen as a whole the page must not be the exact same or damn similar to other internal or external pages). Onpage content should include:
- Subheadlines
- Structured content
- Tables
- Bullet points
- Definition lists / key: value pairs / infoboxes
- Images
- Infographics
- Videos
- Paragraph of text or unique combination of content
- Links to other pages (internal and external)
In general the more diversity of content and the more structure within the content, the better. On a targeted listpage, the list is the main content of the page. List always must be a unique combination of content. The content must fufill the search intent of the user (80% goal) and the business utility (reason for the business why this pages exists, 20% goal of the content).
Schema.org Structured Data
Check if your content fulfils some of the Google supported structured data. If yes, aim to fulfill these specification using JSON/LD markup.
Meta
- canonical: a server-less implementation of the URL logic, every page must have on, created automatically, can be overwritten editorially failsafe for stuff that usually goes wrong with URLs
- meta robots: default “index, follow” can be editorially overwritten to “noindex, follow” if we do not want the page to get indexed
- rel-alternate: necessary if an alternate version of this page (i.e.: language, market specific, amp) with the same targeting exist
Mobile
I and Google strongly recommend a mobile first, responsive setup of all pages.
Links to external resources
- You should link to external webpages that help fulfill the users search intent!
- Link as much as you like to external websites and external pages.If you get direct monetary
valuable consideration for setting outgoing links (paid links) set these links to “nofollow” or “sponsored”. - You must not set any other links or complete pages to “nofollow”.
Ballast / Dead Weight
If a page has no targeted phrase (does not want to get found for anything) or does not fulfill the QC, has no business utility or does not solve the “job to be done” for the user it is dead weight and
- must either not exit (HTTP 404 or HTTP 410 if it existed once, no redirects before errors)
- or must not get indexed (meta robots: noindex)
- is not systematically linked, not referenced onpage and not listed in the sitemap.xml
- no redirects before any errors
There are a lot of reasons why pages exist on a webpage other than SEO. But from an SEO point of view these are dead weight and should not massively get linked and indexed. Pages for brand searches i.e.: [your-brand tos], [you-brand contact] are also valid targeted phrases and should therefore not be treated as ballast. Ballast is only when a page really does not want to get found for anything or anything unqiue on this website.
Startpage
- The startpage must be in the root of the domain. i.e. https://www.example.com/
- Do not redirect away from the startpage.
- The starpage is a targeted page for
- the brand of the webproperty
- one unbranded competitive targeted phrase.
- The startpage must fufill the internal interlinking rules (and visible link to the most important targeted pages).
SEO Data Tools
- Google Search Console
- Verify your site via Domain-Property and URL-Prefix-Property.
- Verify all your URL namespaces as URL-Prefix-Property
- Google Analytics or another onpage analytics alternative
- Page Speed Insights
- Mobile Friendly Test
- Rich snippet testing tool, Structured Data Testing Tool
- Google Lighthouse
- Webpagetest.org
- Franz SEO Livetest Chrome Extension
- Google Trends
- Google Autocomplete (Note: turn off personal results) , Keywordtool.io (free version)
- Redirect Detective